Cosmic Background Radiation Drawing
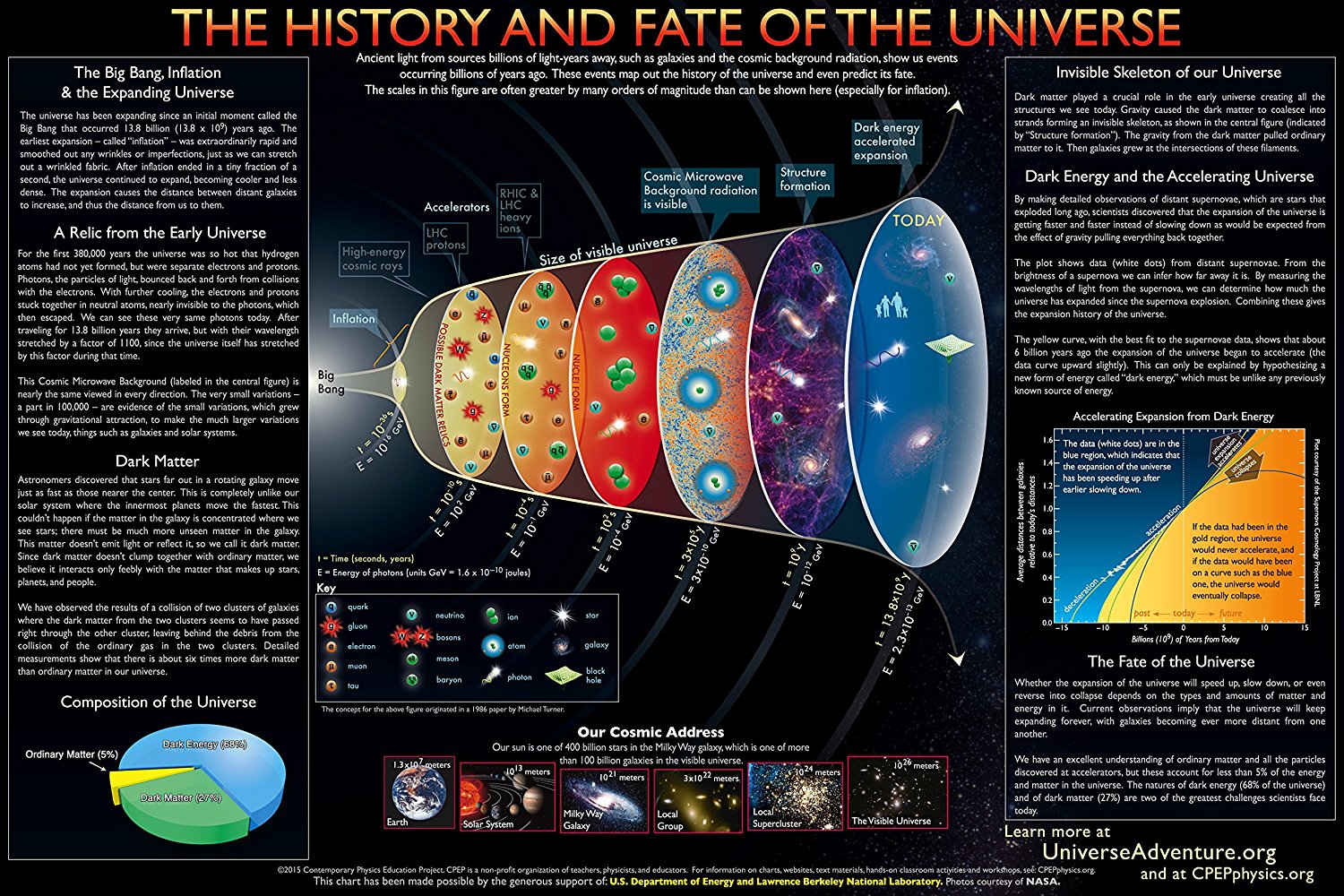
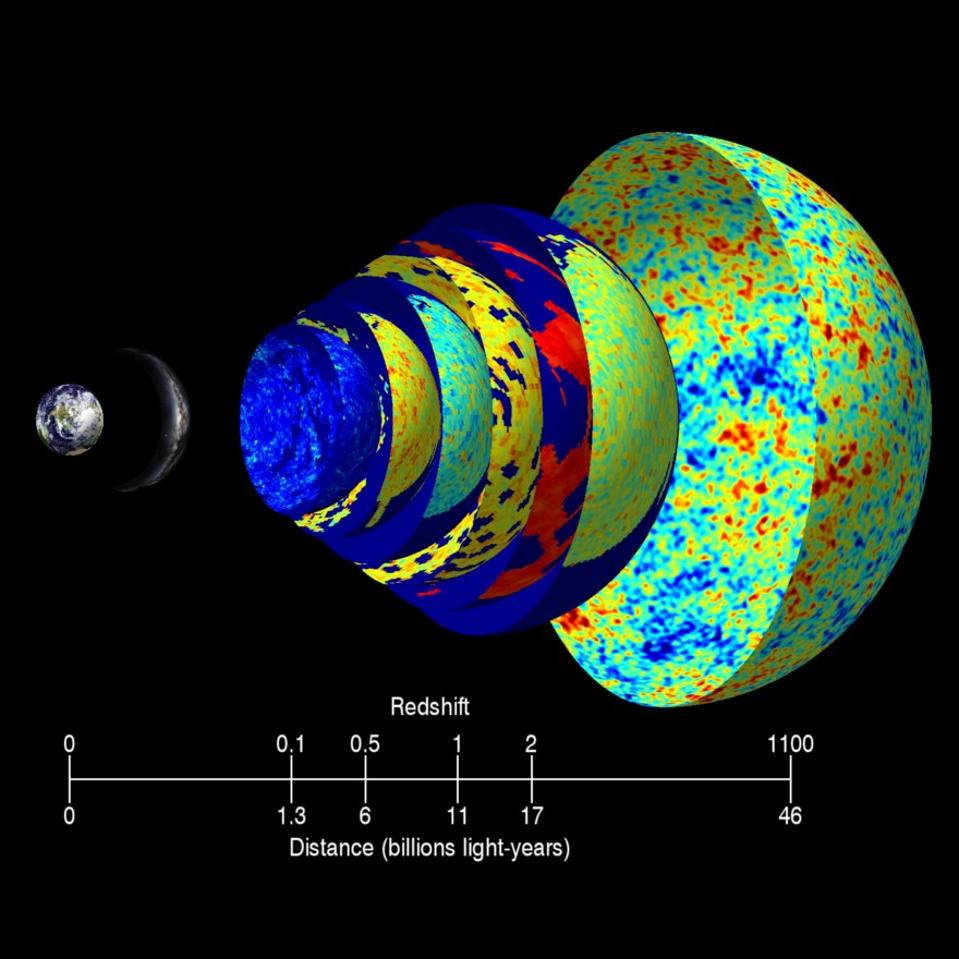
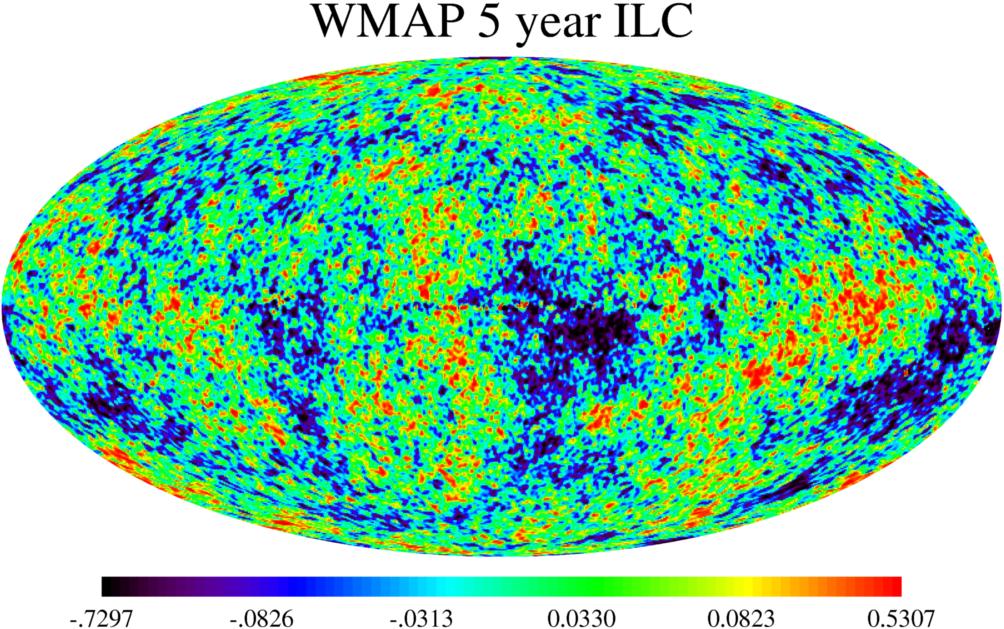
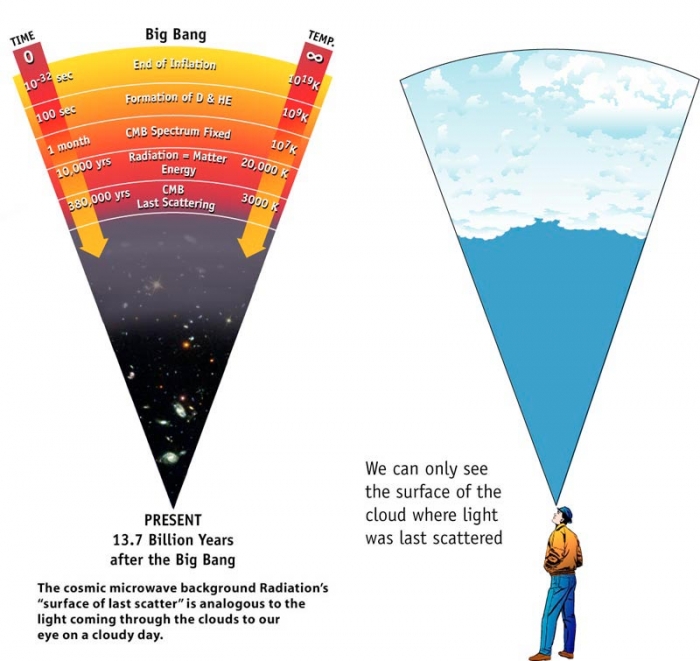
Cosmic Background Radiation Drawing - Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) radiation provides a remarkable window onto the early universe, revealing its composition and structure. Web this lecture is a sketch of the physics of the cosmic microwave background. Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) is leftover radiation from the big bang or the time when the universe began. Because the expanding universe has cooled since this primordial explosion, the. [1] with a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. The wmap spacecraft team won a $3 million breakthrough prize for mapping the cosmic. The boxes show the intensity of the cosmic background radiation as measured at various wavelengths by cobe’s instruments. But the cmb isn’t just. Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) reveals the quantum seeding of the primordial universe, the minute fluctuations of radiation that the big bang spewed into an initially very small universe. However, tiny temperature variations or fluctuations (at the part per million level) can offer great insight into the origin, evolution, and content of the universe. The cosmic microwave background radiation, or cmb for short, is a faint glow of light that fills the universe, falling. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Because the expanding universe has cooled since this primordial explosion, the. Web the cosmic microwave background is the afterglow radiation left over from the hot big bang. How the. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The wmap spacecraft team won a $3 million breakthrough prize for mapping the cosmic. Web the primordial cosmic microwave background (cmb) radiation has since traveled some 13.8 billion years through the expanding cosmos to our telescopes on earth and above it. Web the cosmic background radiation fills all space. The cosmic microwave background radiation, or cmb for short, is a faint glow of light that fills the universe, falling. Web the cosmic background radiation fills all space and is a relic from the big bang that created the universe approximately 18 billion years ago. Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) radiation provides a remarkable window onto the early universe,. The boxes show the intensity of the cosmic background radiation as measured at various wavelengths by cobe’s instruments. [1] with a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. Web these photons from a redshift of 1,090 form the cosmic microwave background. It is a remnant that provides an important source of data on. Its temperature is extremely uniform all over the sky. Or so it first seemed. As the theory goes, when the universe was born it underwent rapid. It is a relic, thermal radiation from a hot dense phase in the early evolution of our universe which has now been cooled by the cosmic expansion to just three degrees above absolute zero.. Its temperature is extremely uniform all over the sky. Or so it first seemed. The observed anisotropy can be divided into four main contributions: Leitch of the university of chicago explains. That light, the cosmic microwave background (cmb) radiation, comes to us from every direction in the sky uniformly. 179k views 12 years ago cosmology and. Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) radiation provides a remarkable window onto the early universe, revealing its composition and structure. The origin of this radiation depends on the region of the spectrum that is observed. One component is the cosmic microwave background. Nobel lecture, 8 december, 1978. Web if we assume that the universe was essentially a black body radiator at the time of the emission of the cosmic background radiation, than at 3000k, the peak emission wavelength is about 960nm, which is in the infrared, already outside of the visible spectrum. But the cmb isn’t just. Web roughly 380,000 years later, after matter (mostly hydrogen) had. Leitch of the university of chicago explains. Nobel lecture, 8 december, 1978. Discuss the properties of this afterglow as we see it today, including its average temperature and the size of its temperature fluctuations. Web these photons from a redshift of 1,090 form the cosmic microwave background. The observed anisotropy can be divided into four main contributions: It is a picture, in false color, of the baby universe, 13.8 billion years ago, when the universe was 370,000 years old. Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) is leftover radiation from the big bang or the time when the universe began. Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) radiation provides a remarkable window onto the early universe, revealing its composition. Its temperature is extremely uniform all over the sky. The origin of this radiation depends on the region of the spectrum that is observed. That light, the cosmic microwave background (cmb) radiation, comes to us from every direction in the sky uniformly. Web here is our most detailed map of the cosmic microwave background, or cmb, as measured by the planck mission. Nobel lecture, 8 december, 1978. The cosmic microwave background radiation, or cmb for short, is a faint glow of light that fills the universe, falling. Because the expanding universe has cooled since this primordial explosion, the. Radio astronomy has added greatly to our understanding of the structure and dynamics of the universe. Web the cosmic microwave background ( cmb or cmbr) is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. One component is the cosmic microwave background. However, tiny temperature variations or fluctuations (at the part per million level) can offer great insight into the origin, evolution, and content of the universe. Web the cosmic microwave background (cmb) is leftover radiation from the big bang or the time when the universe began. Cosmic microwave background (cmb), electromagnetic radiation filling the universe that is a residual effect of the big bang 13.8 billion years ago. Leitch of the university of chicago explains. Web space & physics. Explain why we can observe the afterglow of the hot, early universe.
Cosmic Background Radiation AI Generated Artwork NightCafe Creator

COSMIC BACKGROUND RADIATION WHOLE UNIVERSE THEORY
COSMIC BACKGROUND RADIATION WHOLE UNIVERSE THEORY
Ask Ethan Will The Cosmic Microwave Background Ever Disappear?

The Cosmic Microwave Background Astronomy
CMB

Cosmic Radiation by twocollective on DeviantArt

How To Draw A Cosmic Universe, Cosmic Universe, Step by Step, Drawing
The Cosmic Microwave Background Astronomy 801 Stars
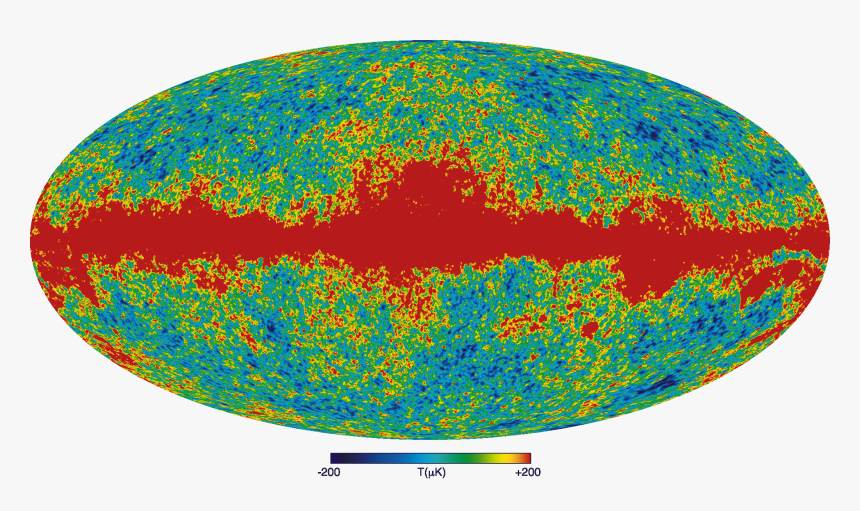
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation, HD Png Download kindpng
Click And Drag Your Mouse Anywhere In The Map To Spin It Around And See The Baby Picture Of The Universe From All.
The Cosmic Microwave Background (Cmb) Radiation, Which We’ve Concluded Is The Leftover Glow From The Big Bang Itself, Is That Key Evidence.
The Solid Line Shows How The Intensity Of Radiation Should Change With Wavelength For A Blackbody With A Temperature Of 2.73 K.
Web If We Assume That The Universe Was Essentially A Black Body Radiator At The Time Of The Emission Of The Cosmic Background Radiation, Than At 3000K, The Peak Emission Wavelength Is About 960Nm, Which Is In The Infrared, Already Outside Of The Visible Spectrum.
Related Post: