Dna Template In Pcr
Dna Template In Pcr - Web to overcome these issues, dna templates can be cleansed by dialysis and precipitation by ethanol. Web as pcr progresses, the dna generated is itself used as a template for replication, setting in motion a chain reaction in which the original dna template is exponentially amplified. This is the enzyme that is in charge of replicating dna. Web preparation of template dna is a critical step in pcr. Short strands of dna that adhere to the target segment. This process results in the duplication of the original dna, with each of the new molecules containing one old and one new strand of dna. Following the aforementioned steps of pcr, the next step includes agarose gel electrophoresis using ethidium bromide. Web rather, pcr involves the synthesis of multiple copies of specific dna fragments using an enzyme known as dna polymerase. A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna. This method allows for the creation of literally billions of dna. This method allows for the creation of literally billions of dna. Pcr happens in three basic steps: A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna. Deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dntps) required cofactor: Web to overcome these issues, dna templates can be cleansed by dialysis and precipitation by ethanol. The only information needed for this fragment to be replicated is the sequence of two short regions of nucleotides (the subunits of dna) at either end of the region of interest. A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna. This method allows for the creation of. A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna. Following the aforementioned steps of pcr, the next step includes agarose gel electrophoresis using ethidium bromide. Web rather, pcr involves the synthesis of multiple copies of specific dna fragments using an enzyme known as dna polymerase. Web preparation. A pcr template for replication can be of any dna source, such as genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna), and plasmid dna. Web to overcome these issues, dna templates can be cleansed by dialysis and precipitation by ethanol. Dna bases (a, t, c and g) are the building blocks of dna and are needed to construct the new strand of. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a method to rapidly amplify sequences of dna. This process results in the duplication of the original dna, with each of the new molecules containing one old and one new strand of dna. Web as pcr progresses, the dna generated is itself used as a template for replication, setting in motion a chain. Several other strategies to clean the dna template include using chloroform for extraction purposes and chromatography. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a biochemical technology in molecular biology used to amplify a single, or a few copies, of a piece of dna across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular dna sequence. The. Dna bases (a, t, c and g) are the building blocks of dna and are needed to construct the new strand of dna. Remember, pcr is a very sensitive technique, so it’s generally safer to add a lower concentration of dna template than you think rather than too much. Dna nucleotide bases (also known as dntps). Web preparation of template. Web pcr is based on using the ability of dna polymerase to synthesize new strand of dna complementary to the offered template strand. Web the integral component is the template dna —i.e., the dna that contains the region to be copied, such as a gene. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a biochemical technology in molecular biology used to. Web polymerase chain reaction or pcr is a technique for amplifying specific dna fragments from a dna template. Following the aforementioned steps of pcr, the next step includes agarose gel electrophoresis using ethidium bromide. Genomic dna, plasmid dna, cdna or purified pcr products can be used as template dna in pcr. They identify the portion of dna to be multiplied. Dna synthesis occurs during various biological events such as cell division, dna repair, and the. Web the dna template to be copied. Web each pcr assay requires the presence of template dna, primers, nucleotides, and dna polymerase. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a method to rapidly amplify sequences of dna. The ingredients are assembled in a tube, along. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a method to rapidly amplify sequences of dna. The only information needed for this fragment to be replicated is the sequence of two short regions of nucleotides (the subunits of dna) at either end of the region of interest. This method allows for the creation of literally billions of dna. Web the key ingredients of a pcr reaction are taq polymerase, primers, template dna, and nucleotides (dna building blocks). During a typical pcr, template dna (containing the region of interest) is mixed with deoxynucleotides (dntps), a dna polymerase and primers. The amplification is achieved by thermostable taq dna polymerase enzyme. Web pcr is based on using the ability of dna polymerase to synthesize new strand of dna complementary to the offered template strand. Web the dna template to be copied. Short strands of dna that adhere to the target segment. Dna nucleotide bases (also known as dntps). Web a standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq polymerase. Web as pcr progresses, the dna generated is itself used as a template for replication, setting in motion a chain reaction in which the original dna template is exponentially amplified. Web each pcr assay requires the presence of template dna, primers, nucleotides, and dna polymerase. As little as one dna molecule can serve as a template. Web pcr is a powerful amplification technique that can generate an ample supply of a specific segment of dna (i.e., an amplicon) from only a small amount of starting material (i.e., dna template or target sequence). In experiments where dna served as an indicator molecule, pcr produced sufficient dna material for the analysis, starting from a sample in which the sequence of interest may have been present in just a single copy.
Fun with Biotechnology PCR

What Is The Template Of The Pcr
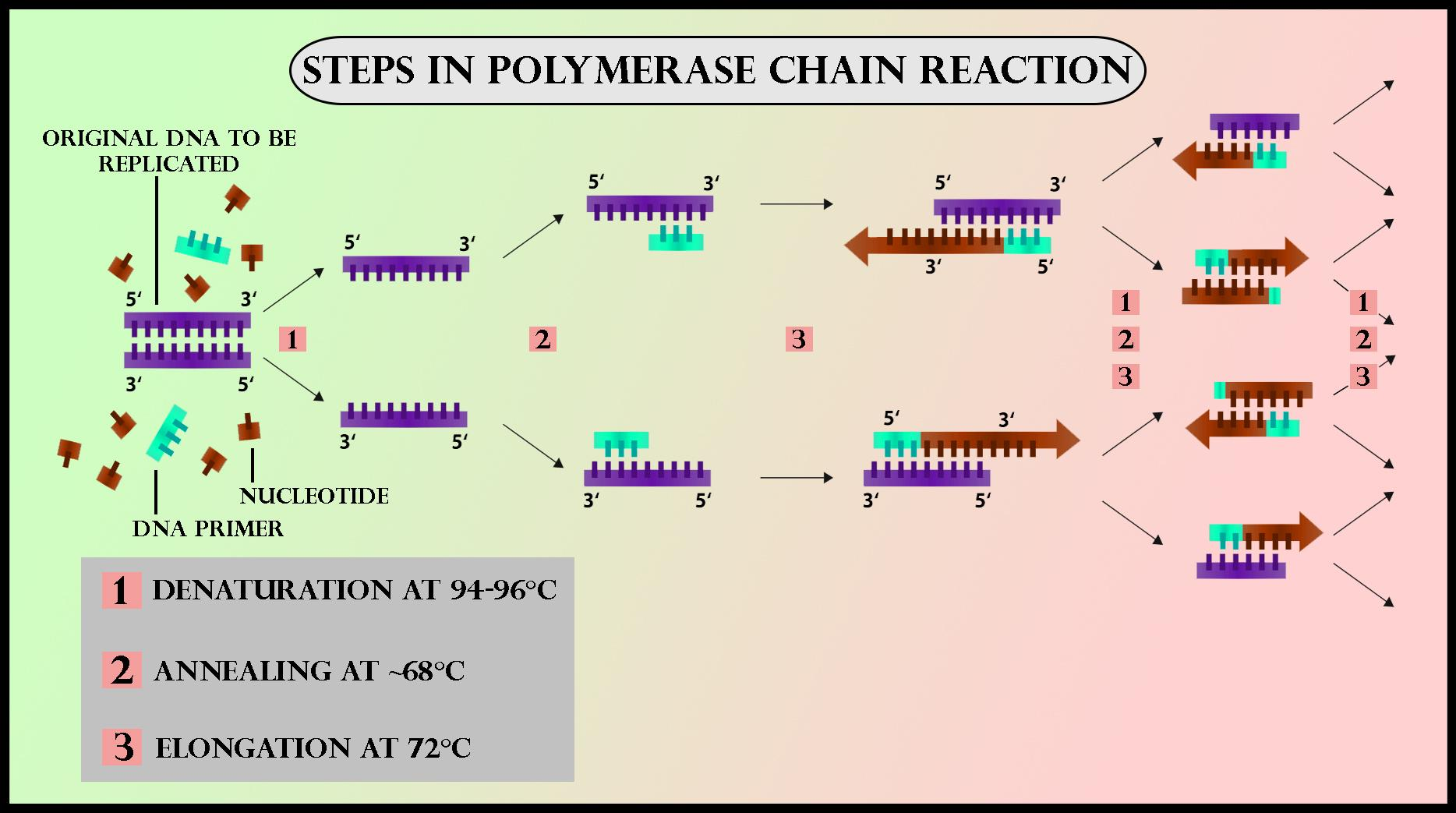
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing steps of PCR?

Parallel DNA polymerase chain reaction Synthesis of two different PCR

What Is The Template Of The Pcr

DNA Template PCR Sanger Sequencing Workflow Management Platform for
Setting up for Success How Do I Ensure I Have the Right Template for
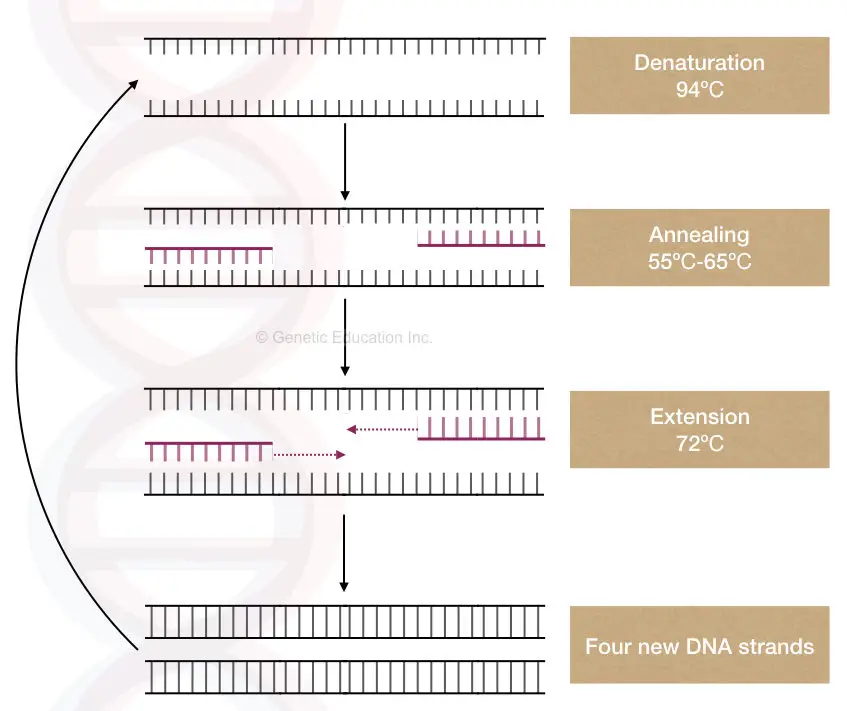
What are the properties of PCR (template) DNA?

PCR Overview GoldBio

How Much Template Dna For Pcr
Web Polymerase Chain Reaction (Pcr) Amplifies The Target Segment Of Dna By Several Orders Of Magnitude Via Repetitive Cycles.
This Is The Biological Sample You Want To Amplify Dna From.
From A Single Copy Of Dna (The Template), A Researcher Can Create Thousands Of Identical Copies Using A Simple Set Of Reagents And A Basic Heating And Cooling.
Web The Integral Component Is The Template Dna —I.e., The Dna That Contains The Region To Be Copied, Such As A Gene.
Related Post: