Draw And Label Cell Cycle
Draw And Label Cell Cycle - Web draw your bead chromosomes in each stage of mitosis. But be sure to accurately indicate the relative sizes and colors of each different chromosome pair. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. You do not need to draw every single bead. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. Interphase represents the portion of the cell cycle. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces two identical (clone. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. During interphase, the cell grows and. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. Web the cell cycle is defined as the events that enable cells to proceed from one cell division event to the next. It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna),. Interphase is followed by the mitotic phase. As completely as possible, list the key events that occur in each stage of mitosis. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two. Cell division itself consists of the overlapping processes of mitosis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm). In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period (interphase) followed by mitosis and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells. During interphase, the cell. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. In this exercise you will make models of chromosomes to study the meiosis chromosome replication and. Web an overview of the cell cycle. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Interphase represents the portion of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Web the cell cycle has two major phases: Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving. Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces two identical (clone. During interphase,. The biology corner (worksheets) cell biology. During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells. Web phases of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. The synthesis phase is where. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. Interphase represents the portion of the cell cycle. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series. Compare your list to your classmates. Web cytokinesis is the division of the cell’s cytoplasm, which forms two new cells. Web phases of the cell cycle. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. Web cytokinesis is the division of the cell’s cytoplasm, which forms two new cells. Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. Cells grow following division and produce proteins and organelles. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. Interphase is the phase where the cell grows, replicates its dna and prepares for division. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Some cells exit the cycle and enter g 0. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells.
The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology
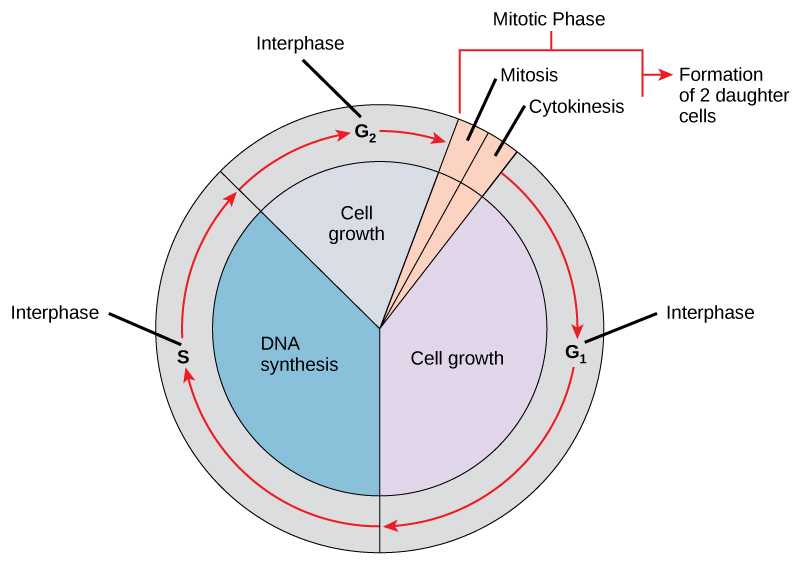
6.2 The Cell Cycle Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

The Cell Cycle Interphase & Mitosis ALevel Biology Revision Notes
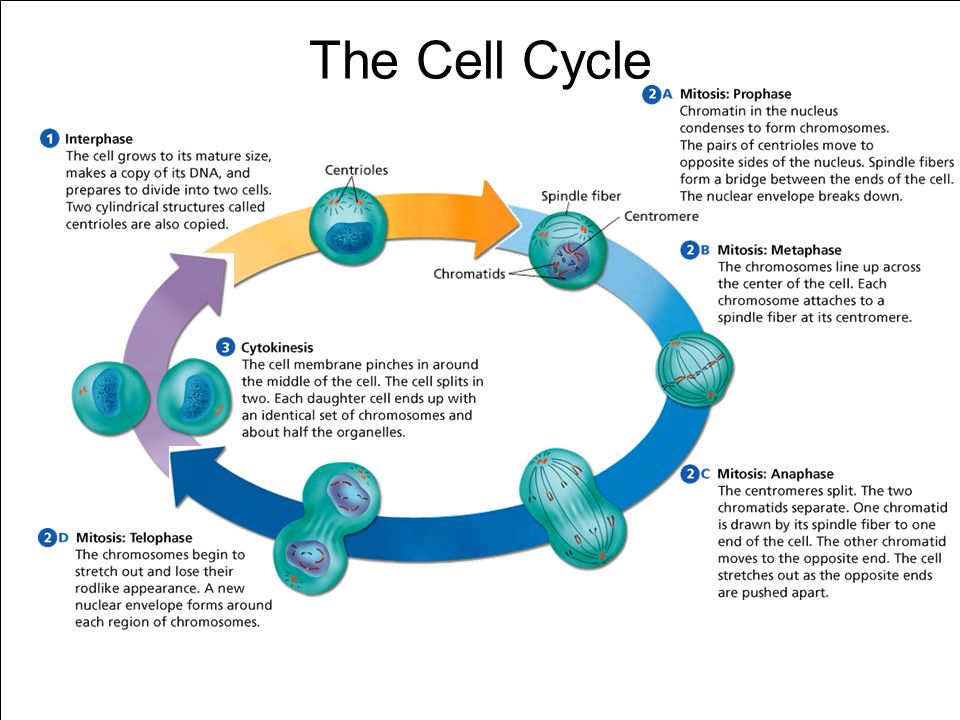
Cell Cycle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download

Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes Leverage Edu

Diagram Of Cell Cycle exatin.info

Cell Cycle Phase Definition, Fours phases of Cell cycle Division
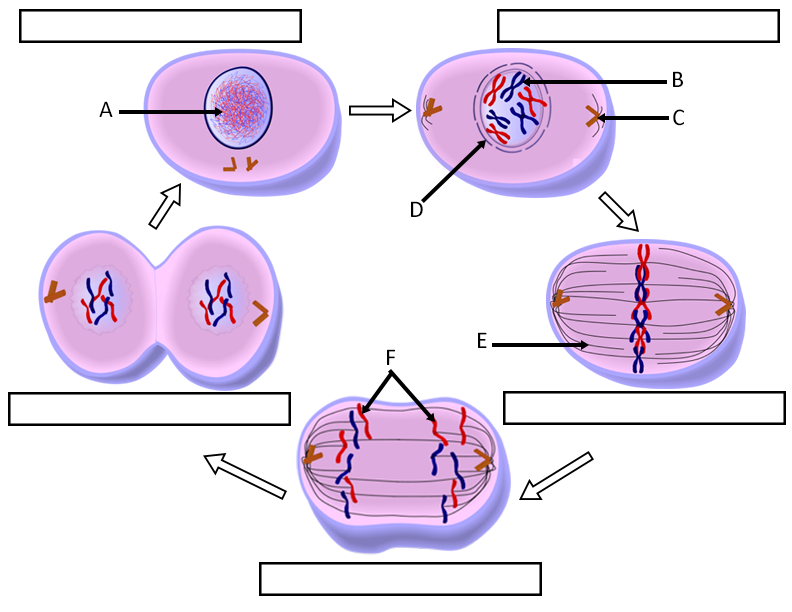
Cell Cycle Labeling
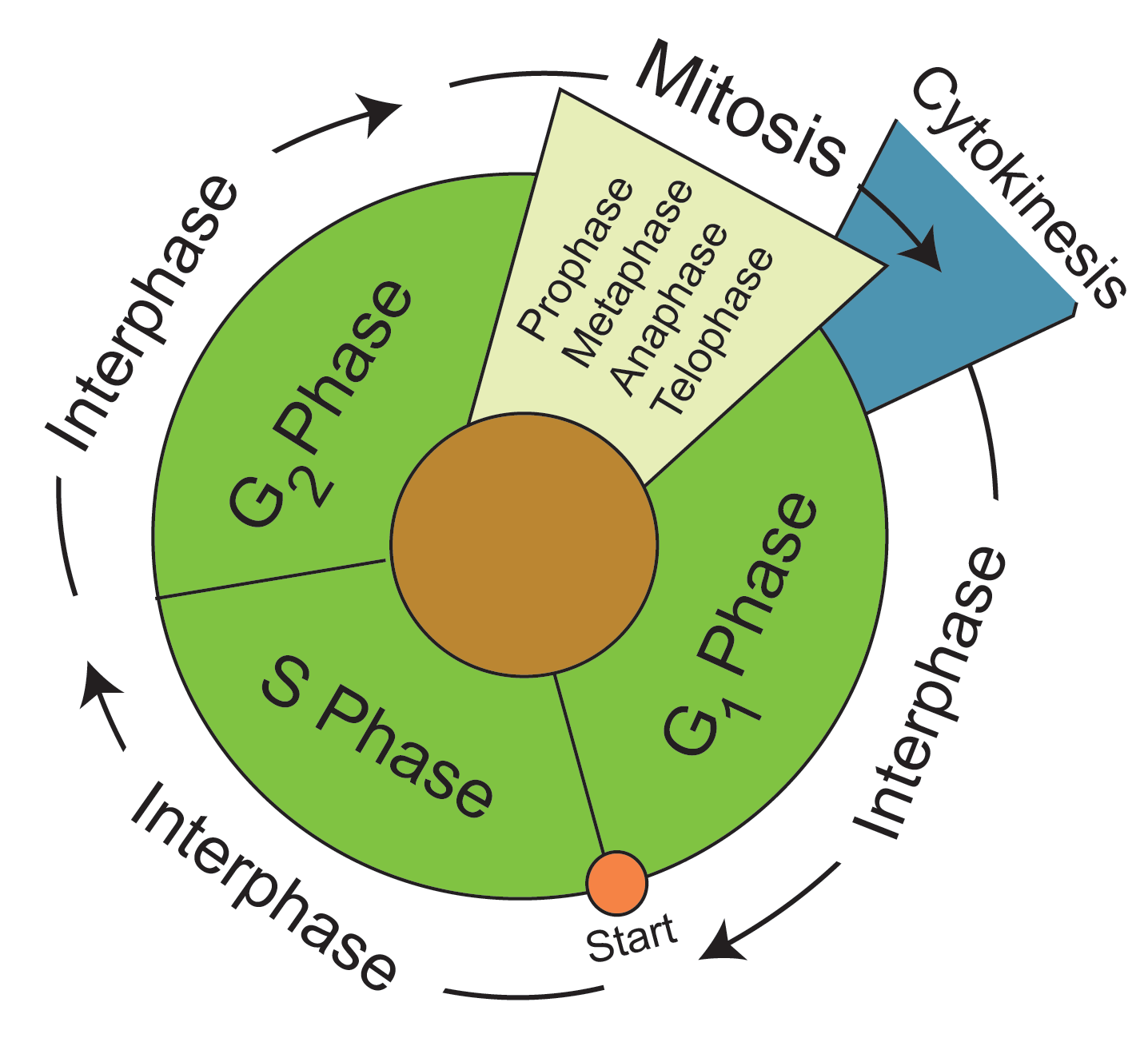
Cell Cycle Phases , Diagram , Types and Comparison

Cell Division An Intro AmoebaMike
During The Mitotic Phase, The Duplicated Chromosomes Are Segregated And Distributed Into Daughter Nuclei.
Web Stages Of The Cell Cycle.
Web The Cell Cycle Describes An Orderly Sequence Of Events That Are Highly Regulated.
In Eukaryotic Cells, The Cell Cycle Is Divided Into Two Major Phases:
Related Post: