Draw Cellular Respiration
Draw Cellular Respiration - C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose) + 6o 2 (oxygen) → 6co 2 (carbon dioxide) + 6h 2 o (water) + 36 atp. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle; Web cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate (atp), which contains energy. This type of cellular respiration occurs in the absence of free oxygen, producing acid or alcohol as the end product. The cellular respiration equation is as follows: The process has three main parts: Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. How do trees help you breathe? Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). Web learn how to draw the cellular respiration diagram and write the equation for cellular respiration. Electron carriers, also called electron shuttles, are small organic molecules that play key roles in cellular respiration. And you need oxygen to breathe. It includes glycolysis, the tca cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the process of pyruvate oxidation and identify its reactants and products. Here is the definition of aerobic respiration, its significance, the organisms that rely on it, and. 8.1.4 explain aerobic respiration, including the link reaction, the krebs cycle, the role of nadh + h +, the electron transport chain and the role of oxygen. Glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Though it releases only 2 atps, it occurs more quickly than aerobic respiration. Electron carriers, also called electron shuttles, are small organic molecules that play. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process. Describe the process of glycolysis and identify its reactants and products. It includes glycolysis, the tca cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration takes the energy stored in glucose and transfers it to atp. Describe the process of pyruvate oxidation. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. Web cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate. Cellular respiration is one of the most elegant, majestic, and fascinating metabolic pathways on earth. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. Web the energy released is in the form of atp molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell. Web cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into. 8.1.3 draw and label a diagram showing the structure of a mitochondrion as seen in electron micrographs. C6h12o6 + o2 ――> h2o + co2 + 36atp. Though it releases only 2 atps, it occurs more quickly than aerobic respiration. Provide a concise summary of the process. It is the first of six animations about cellular respiration. Web cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into atp, and then release waste products. Glucose is used in cellular respiration. Web how to draw cellular respiration diagram in easy way. It includes glycolysis, the tca cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Anabolic reactions use. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process. 8.1.3 draw and label a diagram showing the structure of a mitochondrion as seen in electron micrographs. It includes glycolysis, the tca cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Web biology i laboratory manual. And you need oxygen to breathe. Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in a living organism. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process. How do trees help you breathe? This animation shows how glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate through a series of enzyme reactions. Web respiration is a fundamental process that occurs in cells that extracts energy. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Web there are three main steps of cellular respiration: C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose) + 6o 2 (oxygen) → 6co 2 (carbon dioxide) + 6h 2 o (water) + 36. Web when organic fuels like glucose are broken down using an electron transport chain, the breakdown process is known as cellular respiration. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process. This type of cellular respiration occurs in the absence of free oxygen, producing acid or alcohol as the end product. Web there are three main stages of cellular respiration: To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Web cellular respiration takes the energy stored in glucose and transfers it to atp. C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose) + 6o 2 (oxygen) → 6co 2 (carbon dioxide) + 6h 2 o (water) + 36 atp. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts. And you need oxygen to breathe. These animations bring to life the molecular engines inside mitochondria that generate atp, the main source of chemically stored energy used. Cellular respiration is one of the most elegant, majestic, and fascinating metabolic pathways on earth. 8.1.3 draw and label a diagram showing the structure of a mitochondrion as seen in electron micrographs. The overall equation for aerobic cellular respiration is: The tca cycle and oxidative phosphorylation require oxygen, while glycolysis can occur in anaerobic conditions. Web cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate (atp), which contains energy. Web cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp.
Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Equation
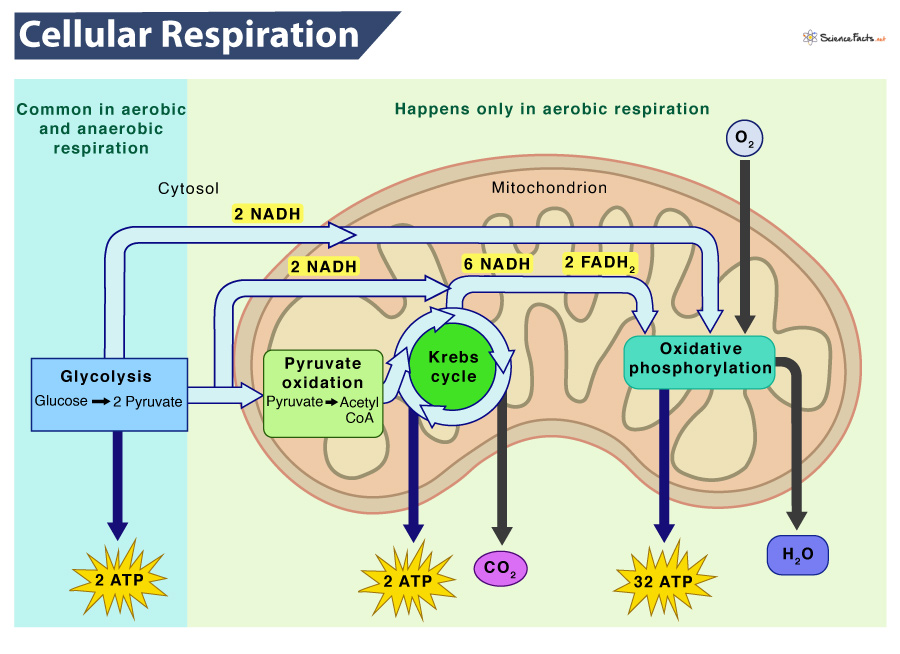
Cellular Respiration Definition, Types, Equations & Steps

Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Schéma de l'illustration de la respiration cellulaire Image Vectorielle

Incredible Cellular Respiration Cycle Diagram References Bigmantova

How To Draw Cellular Respiration Diagram in Easy Way YouTube

Cellular Respiration GCSE Biology Revision

Cellular Respiration Formula Equation
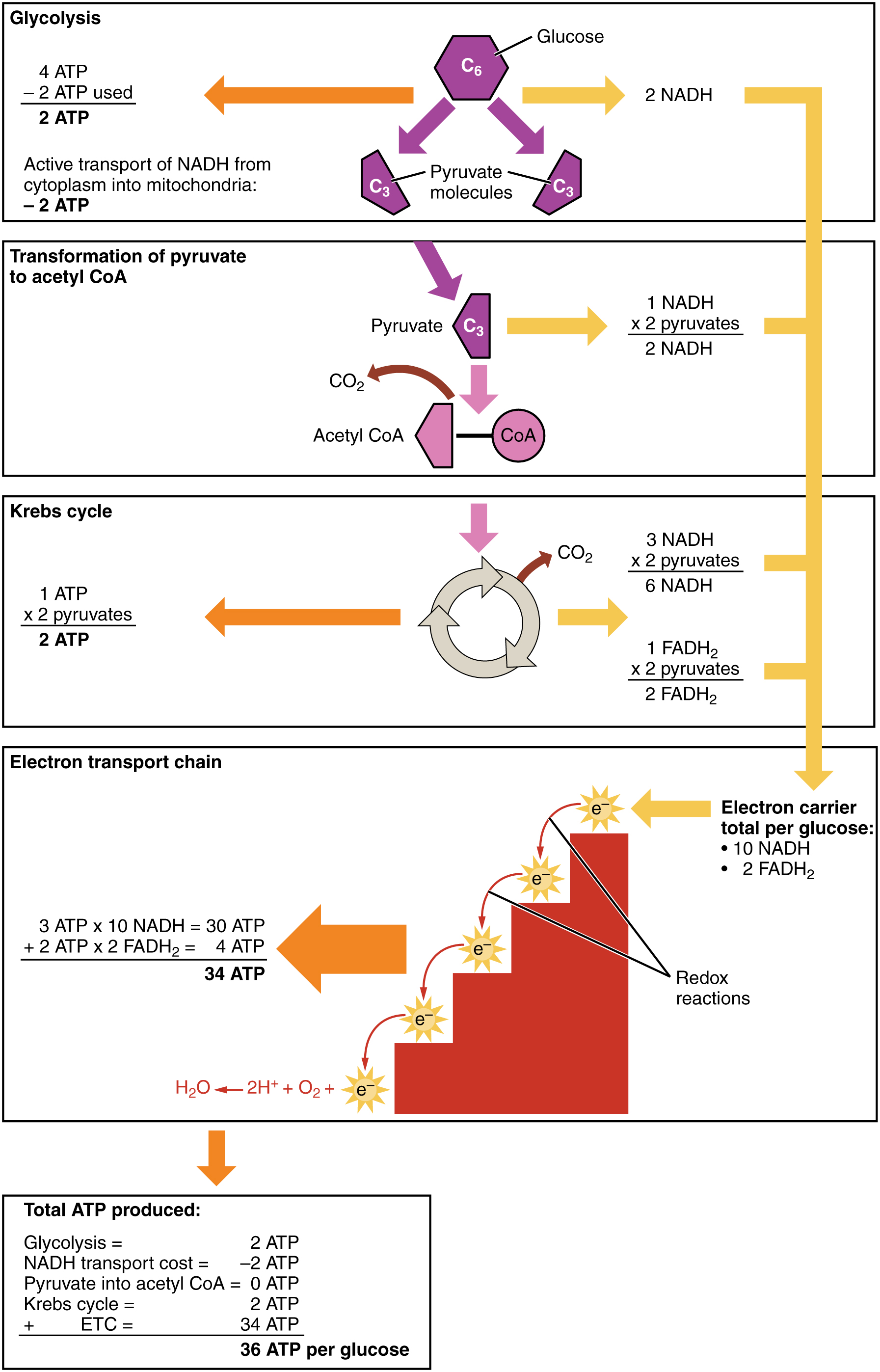
4.10 Cellular Respiration Human Biology
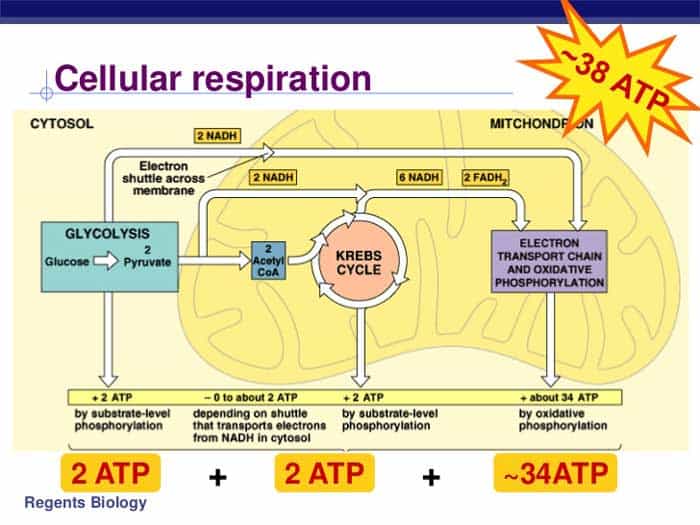
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams
The Cellular Respiration Equation Is As Follows:
Web The Energy Released Is In The Form Of Atp Molecules That Are Used To Carry Out Various Functions Of The Cell.
These Reactions Can Be Catabolic Or Anabolic.
Cellular Respiration Can Occur Both Aerobically (Using Oxygen), Or Anaerobically (Without Oxygen).
Related Post: