How To Draw Velocity Graph From Position Graph
How To Draw Velocity Graph From Position Graph - Graph the slope of each part in the. To find the deceleration, one needs to use the formula change in velocity/time. Web ask students to use their knowledge of position graphs to construct velocity vs. It explains how to use area. Web this video shows how we can take a graph of the position of a moving object and construct a graph of its velocity. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. The shapes of each graph relate by slope. Alternatively, provide an example of a velocity vs. Using the graph to determine displacement, distance, average velocity, average speed, instantaneous velocity, and instantaneous speed. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c) throughout the interval. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. Click here to donate to ophysics.com to help keep the site going. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. The three motion graphs a high school physics student needs to know are: Then, you can use the velocity. Web in this simulation you adjust the shape of a velocity vs. The shapes of each graph relate by slope. Web the position now, after 2 seconds is 8m + 2.3m, which equals to 10.3m. The three motion graphs a high school physics student needs to know are: Why is a deer chasing a cheetah? I am having trouble converting an angular v vs. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. It is found by drawing a straight line tangent to the curve at the point of interest and taking the slope of this straight line. Then, you can use the velocity and the initial position to calculate. The formula for calculating slope is rise over run: Want to join the conversation? Click on the parts of the curve in this graph that correspond to the car not moving (zero speed). I am having trouble converting an angular v vs. Alternatively, provide an example of a velocity vs. To find the deceleration, one needs to use the formula change in velocity/time. Use the graph to answer the following questions. Web given a velocity vs time graph, how do you draw a position vs time graph? Web this video shows how we can take a graph of the position of a moving object and construct a graph of its. To find the deceleration, one needs to use the formula change in velocity/time. The formula for calculating slope is rise over run: Why is a deer chasing a cheetah? It is found by drawing a straight line tangent to the curve at the point of interest and taking the slope of this straight line. The graph below records the position. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. Web the position now, after 2 seconds is 8m + 2.3m, which equals to 10.3m. Want to join the conversation? Graph the slope of each part in the. It explains how to use area. (change in position) / (change in time). Why is a deer chasing a cheetah? The three motion graphs a high school physics student needs to know are: Web given a velocity vs time graph, how do you draw a position vs time graph? It explains how to use area. It explains how to use area. Click here to donate to ophysics.com to help keep the site going. A steeper slope indicates higher velocity, while a gentle slope indicates slower velocity. Is there a way to do it with the graph alone (no calculus)? Graph the slope of each part in the. Alternatively, provide an example of a velocity vs. A steeper slope indicates higher velocity, while a gentle slope indicates slower velocity. The shapes of each graph relate by slope. Web given a velocity vs time graph, how do you draw a position vs time graph? Click on the parts of the curve in this graph that correspond to the car. To find the deceleration, one needs to use the formula change in velocity/time. Then, you can use the velocity and the initial position to calculate the position at that time using the formula d = v*t + d 0 , where d is the position, v is the velocity, t is the time. The formula for calculating slope is rise over run: (change in position) / (change in time). A steeper slope indicates higher velocity, while a gentle slope indicates slower velocity. Watch how the graphs of position vs. Time graph by sliding points up or down. Alternatively, provide an example of a velocity vs. Web this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs, and acceleration time graphs. Web this video shows how we can take a graph of the position of a moving object and construct a graph of its velocity. Web motion graphs, aka kinematic curves, are a common way to diagram motion in physics. Use the graph to answer the following questions. Web ask students to use their knowledge of position graphs to construct velocity vs. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c) throughout the interval. Web given a velocity vs time graph, how do you draw a position vs time graph? I am having trouble converting an angular v vs.
Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts
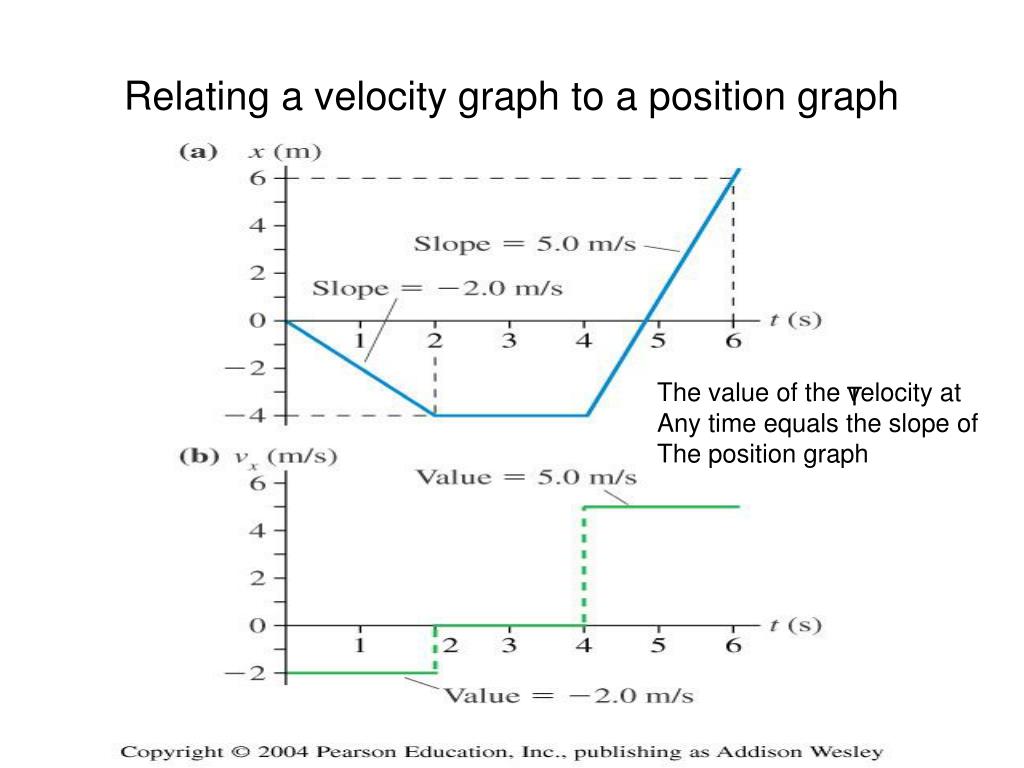
PPT Chapter 2 Kinematics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

Drawing a velocity graph from a position graph YouTube

Drawing a position graph from a velocity graph YouTube

Constant Acceleration How to Make a Velocity Graph from a Position

Velocity time graphs (Video) PhysicsTube
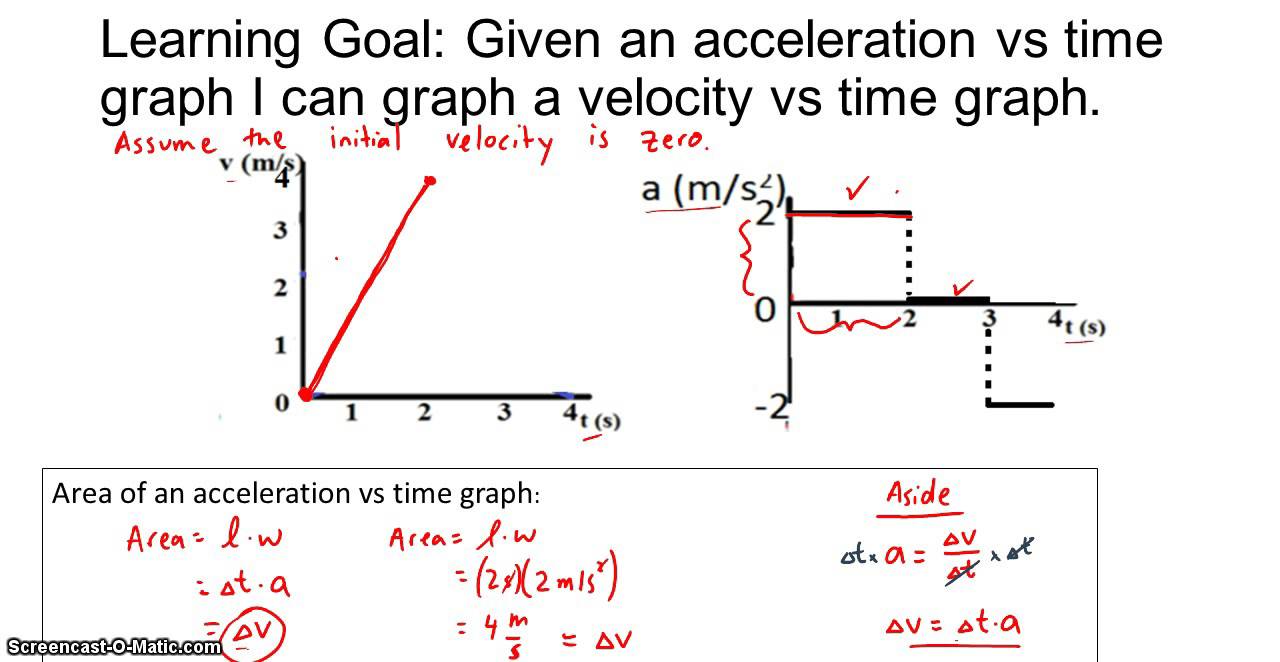
Drawing Velocity Graphs Given Acceleration Graphs YouTube
Velocity time graph, Displacement time graph & Equations Physics

position graphs from velocity graphs YouTube
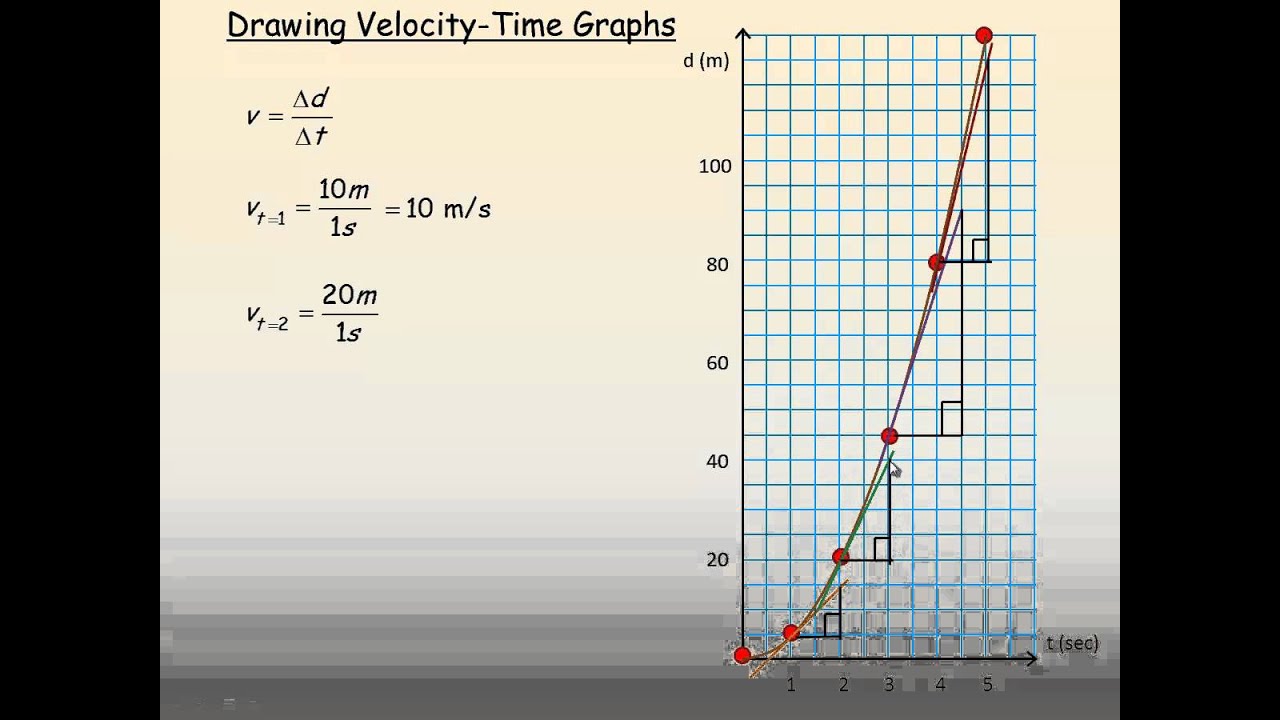
Drawing VelocityTime Graphs YouTube
Time Change As They Adjust To Match The Motion Shown On The Velocity Vs.
The Shapes Of Each Graph Relate By Slope.
What’s Missing From The Graph Being Drawn In The Picture Above?
Using The Graph To Determine Displacement, Distance, Average Velocity, Average Speed, Instantaneous Velocity, And Instantaneous Speed.
Related Post: