Muscle Contraction Drawing
Muscle Contraction Drawing - What are the steps in muscle contraction? Web muscle contractions are defined by changes in the length of the muscle during contraction. Classify the different types of muscle tissue. Web muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. Web describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. The whole process is called the mechanism of muscle contraction and it can be summarized in three steps: The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. Web choose from muscle contraction drawing stock illustrations from istock. Compare and contrast concentric and eccentric contraction. As long as ca ++ ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten. Compare and contrast isotonic and isometric contraction. 1.3m views 14 years ago. The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. At full contraction, the thin and thick filaments have the most amount of. Web muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the. Compare and contrast isotonic and isometric contraction. As long as ca ++ ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten. Web describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Web how do the bones of the human skeleton move? Explain the role of muscles in. The whole process is called the mechanism of muscle contraction and it can be summarized in three steps: The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: Sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Web muscle contraction requires energy, and when atp is broken down, heat is produced. The a band stays the same width. As long as ca ++ ions remain in the sarcoplasm to bind to troponin, and as long as atp is available, the muscle fiber will continue to shorten. During contraction, myosin myofilaments ratchet over actin myofilaments contracting the sarcomere. This diagram represents the sequence of events that occurs when a motor neuron stimulates a muscle fiber to contract. Web the. Compare and contrast concentric and eccentric contraction. At full contraction, the thin and thick filaments have the most amount of. The whole process is called the mechanism of muscle contraction and it can be summarized in three steps: Web muscle contractions are defined by changes in the length of the muscle during contraction. You can take the amount of force. Web muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Skeletal muscles contract and relax to mechanically move the body. Web describe the components involved in a muscle contraction; Web describe the components involved in a. Web at its simplest, the neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse where neuronal signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with skeletal muscle fibers, causing them to contract. This heat is very noticeable during exercise, when sustained muscle movement causes body temperature to rise, and in cases of extreme cold, when shivering produces random skeletal muscle contractions to. This makes the sarcomeres shorter and thicker, contracting the muscle. Web the strength of a muscle’s contraction can be controlled by two factors: Explain how muscles contract and relax; Web muscle contraction requires energy, and when atp is broken down, heat is produced. Slow twitch and fast twitch muscle fibers. Neuromuscular junction and motor unit. You can take the amount of force of each actin myosin pair (from wikipedia) and multiply it to check the actual forces produced. It can be uncomfortable and painful at. At full contraction, the thin and thick filaments have the most amount of. Sliding filament model of muscle contraction. 1.3m views 14 years ago. Web at its simplest, the neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse where neuronal signals from the brain or spinal cord interact with skeletal muscle fibers, causing them to contract. The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. Explain the role of muscles in locomotion. Sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Web muscle contractions are defined by changes in the length of the muscle during contraction. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: Skeletal muscles contract and relax to mechanically move the body. Explain the role of muscles in locomotion. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Describe the sliding filament model of muscle contraction What are the steps in muscle contraction? Muscles allow for motions such as walking, and they also facilitate bodily processes such as respiration and digestion. The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. Isotonic contractions generate force by changing the length of the muscle and can be concentric contractions or eccentric contractions. The sarcomere is the region in which sliding filament contraction occurs. Neuromuscular junction and motor unit. Explain how muscles contract and relax; Spasticity can make it difficult to: This makes the sarcomeres shorter and thicker, contracting the muscle. When the cns sends a signal, the thick and thin myosin filaments form a “crossbridge” pattern by sliding past each other.
Muscle Contraction and Boundless Biology

Muscle contraction Higher Level Biology IB

Simplifying Muscle Contractions 3D Muscle Lab

Muscle Contraction Vector & Photo (Free Trial) Bigstock
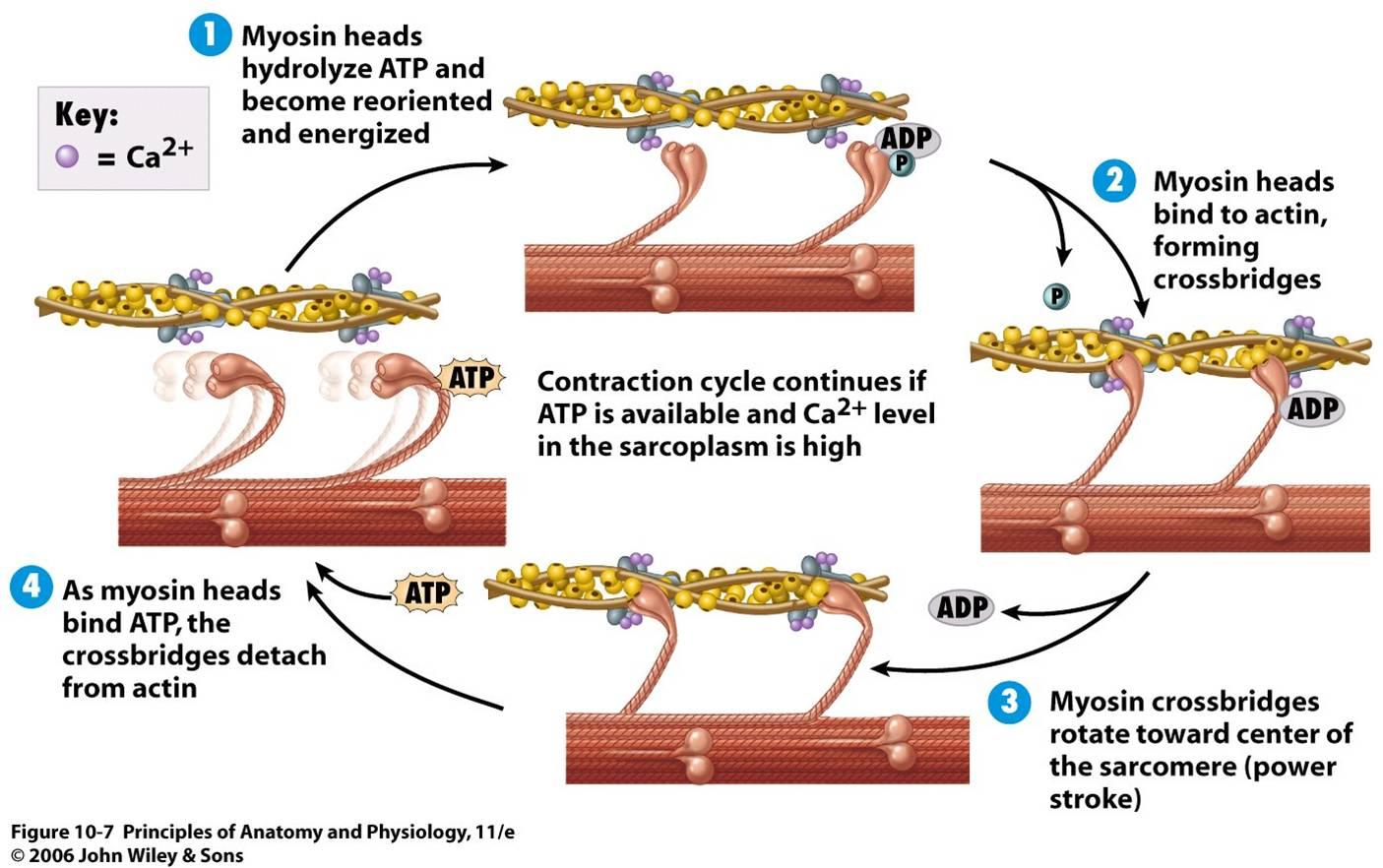
Steps Of Muscle Contraction Diagram

Muscle Contraction Definition, Proteins, Types, Steps

Muscle Contraction Diagram (labelled) Stock Image C043/4842

6.4 Muscle Contraction Medicine LibreTexts
How Do Muscles Contract Steps to Muscle Contraction
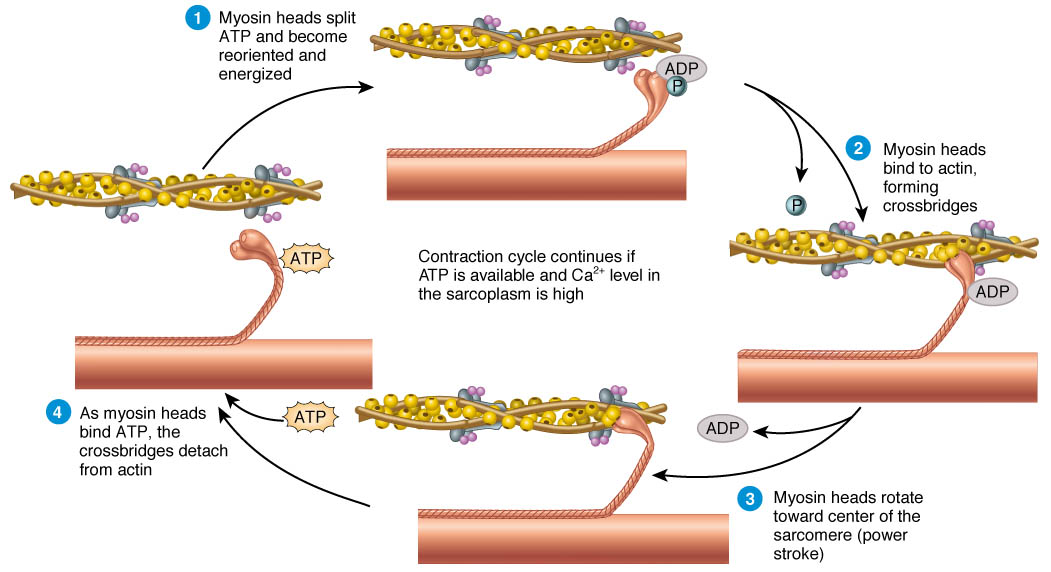
Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction Online Biology Notes
Differentiate Among The Types Of Muscle Contractions.
Web How Do The Bones Of The Human Skeleton Move?
Describe The Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction
Web At Its Simplest, The Neuromuscular Junction Is A Type Of Synapse Where Neuronal Signals From The Brain Or Spinal Cord Interact With Skeletal Muscle Fibers, Causing Them To Contract.
Related Post: