Nucleic Acid Drawing Biology
Nucleic Acid Drawing Biology - How does the structure of nucleic acids allow hereditary information to be stored? Describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. Lecture for introductory biology for science majors. Explain rna’s structure and roles. Web oregon state university. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Here, we’ll just take a quick look at nucleic acids from the macromolecule perspective. The nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. Other file formats can be used via the molecular sketcher. A web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. Each of the sugar groups in the backbone is attached (via the bond shown in red) to a third type of molecule called a nucleotide base: A biological macromolecule comprised of monomers of nucleotides. Describe the structure of nucleic acids and define the two types of nucleic acids. It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotes and in the chloroplasts. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Explain rna’s structure and roles. 55 views 1 year ago scherr lectures biology i. Or open an rna 2d json schema. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ). However, manually drawing structures is laborious and infeasible for structures thousands of nucleotides long. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. The nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. How does the structure of nucleic acids allow hereditary information to be. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: A biological macromolecule comprised of monomers of nucleotides. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. A common thread of nucleic acid aptamers with noncanonical structures, which makes them very promising for therapeutic applications, is their uniqueness, flexibility, and binding. They carry. Web a nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems. Describe nucleic acids’ structure and define the two types of nucleic acids. A nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: Each of the sugar groups in the backbone. Geometrically strict drawing of nucleic acid structures with graphical structure editing and highlighting of complementary subsequences. Each of the sugar groups in the backbone is attached (via the bond shown in red) to a third type of molecule called a nucleotide base: Explain the structure and role of dna. Web nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity. A nucleotide is made up of three components: Each of the sugar groups in the backbone is attached (via the bond shown in red) to a third type of molecule called a nucleotide base: Explain the structure and roles of rna. Dna is the genetic material found in all living organisms. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic. 55 views 1 year ago scherr lectures biology i. How does the structure of dna facilitate accurate replication? It is found in the nucleus of eukaryotes and in the chloroplasts and mitochondria. Geometrically strict drawing of nucleic acid structures with graphical structure editing and highlighting of complementary subsequences. By the end of this section, you will be able to do. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Web chemical biology and nucleic acid chemistry. Each of the sugar groups in the backbone is attached (via the bond shown in red) to a third type of molecule called a nucleotide base: The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and. A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of nucleotides. Here, we’ll just take a quick look at nucleic acids from the macromolecule perspective. Guiding questions help students view the content of the syllabus through the conceptual lenses of both the themes and the levels of biological organization. Web indeed, therapeutic. Lecture for introductory biology for science majors. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of. A nucleotide is made up of three components: They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Here, we’ll just take a quick look at nucleic acids from the macromolecule perspective. It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. Describe the structure of nucleic acids and define the two types of nucleic acids. Describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. Or by drawing them in the sketcher. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Explain rna’s structure and roles. Explain dna’s structure and role. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. Web nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life.
Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types

19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotides-5c253d8cc9e77c0001d9b089.jpg)
Nucleic Acid Quick Facts
/DNAstructure-58c233583df78c353c23dbe6.jpg)
Nucleic Acids Types, Structure, and Function
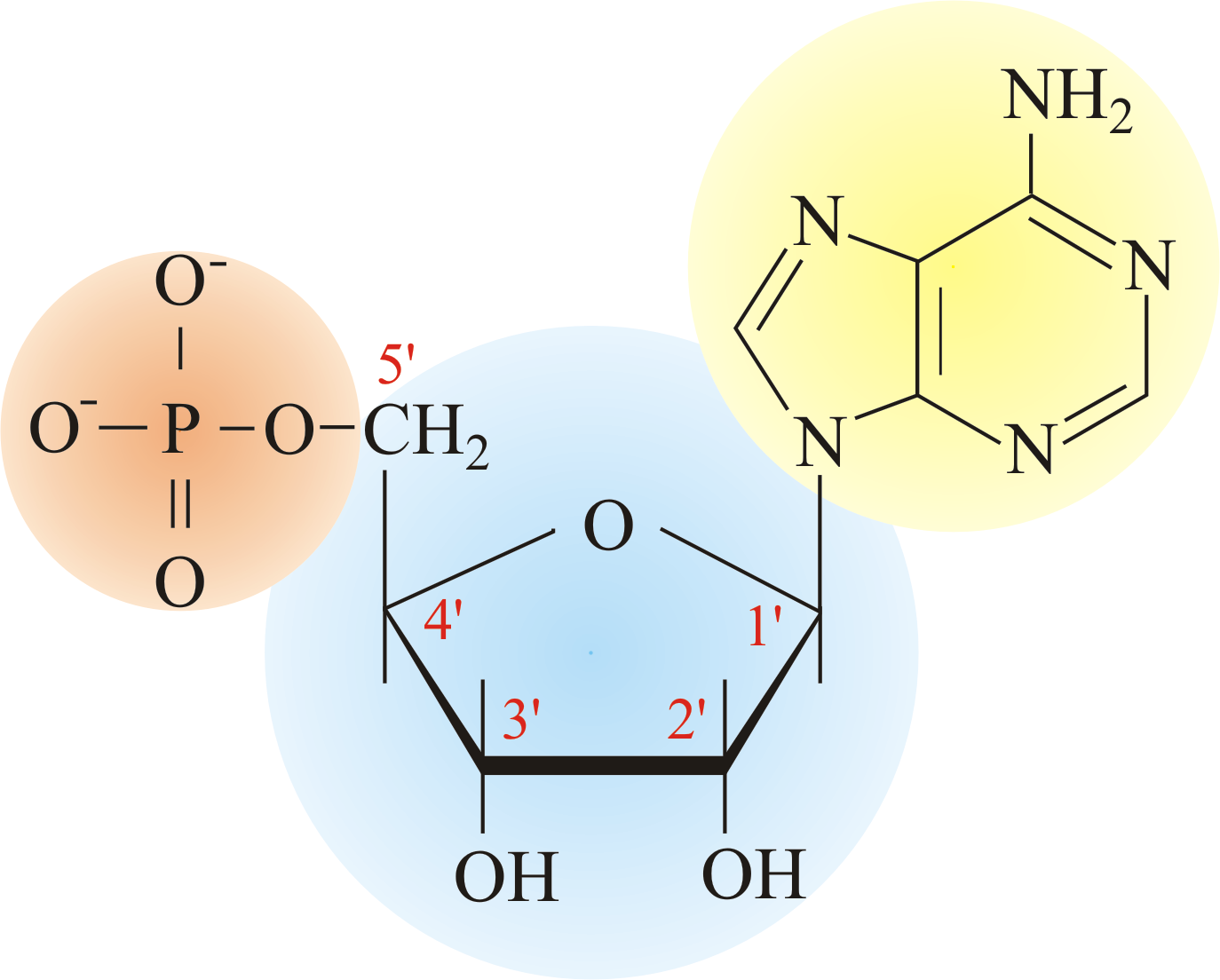
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal

Nucleic Acids DNA And RNA ALevel Biology Revision Notes

nucleic acid classification (lesson 0972) TQA explorer

Nucleic acid Definition, Function, Structure, & Types Britannica
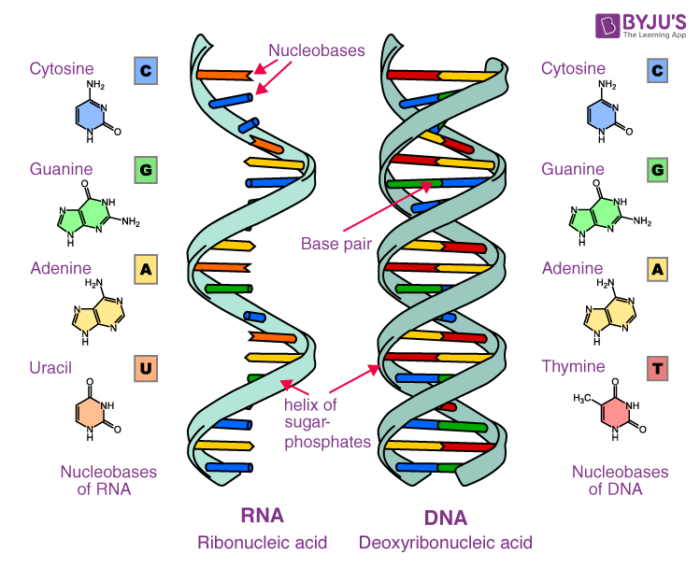
Describe the Roles of Nucleic Acids Dna and Rna
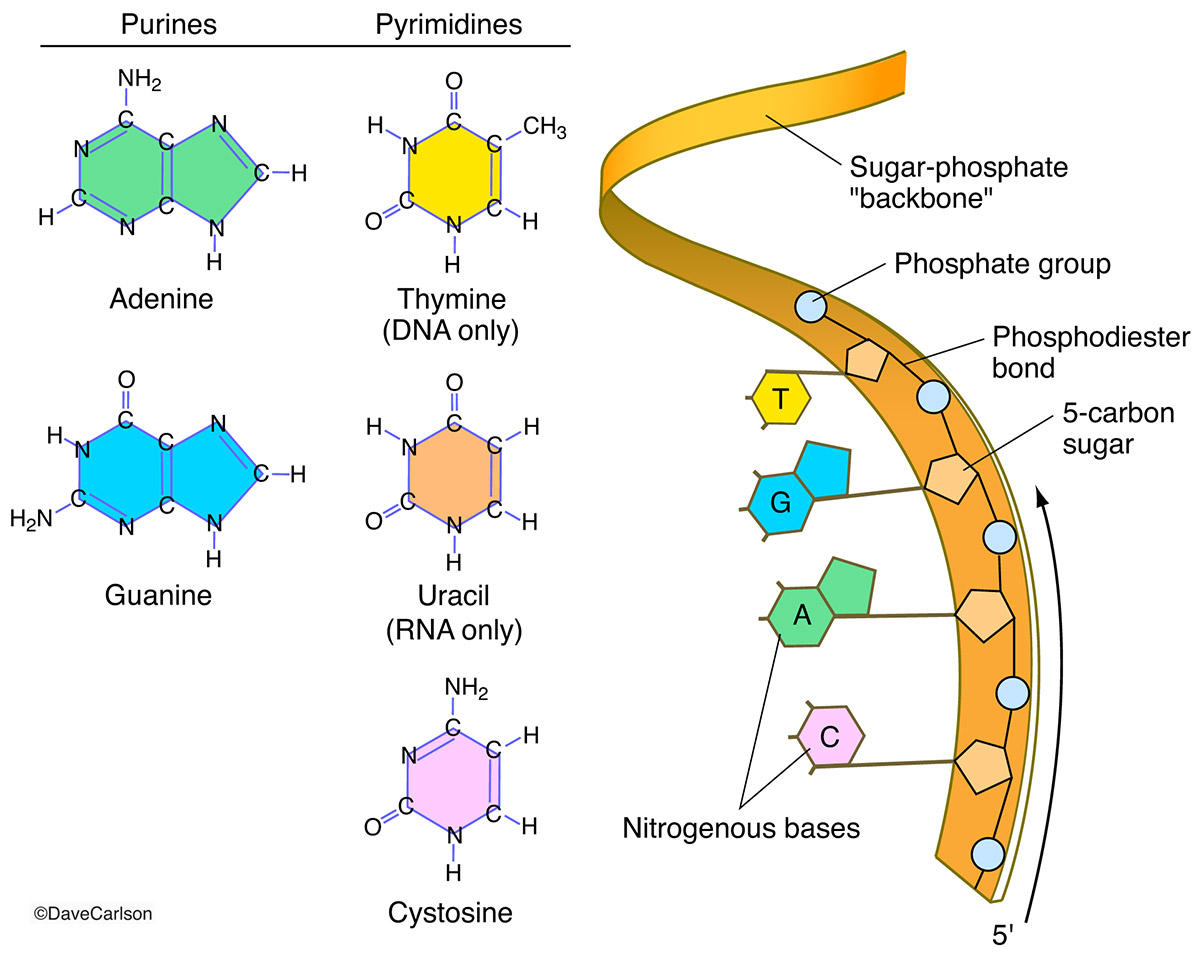
Nucleic Acid Structure Carlson Stock Art
Guiding Questions Help Students View The Content Of The Syllabus Through The Conceptual Lenses Of Both The Themes And The Levels Of Biological Organization.
Web A Web App For Drawing And Exploring Nucleic Acid Structures.
However, Manually Drawing Structures Is Laborious And Infeasible For Structures Thousands Of Nucleotides Long.
Nucleic Acids Are The Most Important Macromolecules For The Continuity Of Life.
Related Post: