Printable Blooms Taxonomy
Printable Blooms Taxonomy - Bloom was an american educational psychologist who is best remembered for his significant contributions to the theory of mastery learning, as well as this renowned and widely used taxonomy. Discover a list of action verbs that you can use to form learning objectives. Web bloom’s taxonomy is a system of hierarchical models (arranged in a rank, with some elements at the bottom and some at the top) used to categorize learning objectives into varying levels of complexity (bloom, 1956). Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. In 1956, benjamin bloom with collaborators max englehart, edward furst, walter hill, and david krathwohl published a framework for categorizing educational goals: Web this taxonomy of educational objectives gets its name from its creator, benjamin bloom. The framework elaborated by bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: Web a taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing, abridged edition. Knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Web additional information about bloom’s revised taxonomy is available here: Examining and breaking information into parts by identifying motives or causes; *contents of this list compiled from the work of: Web “since its publication in 1956, bloom’s taxonomy has been a foundation of most modern education systems. The outcome of this study was bloom’s taxonomy of learning (1956). Web additional information about bloom’s revised taxonomy is available here: Web solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. The theory is based upon the idea that there are levels of observable actions that indicate something is happening in the brain (cognitive activity.) by creating learning objectives using. Solving problems by applying acquired knowl‐ edge, facts, techniques and rules in a. Web bloom’s taxonomy is a hierarchical model that outlines six categories of learning and application skills that progress from less to more complex. Knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Web a taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing, abridged edition. Examining and breaking information into parts by identifying motives or causes; The framework elaborated by bloom and his collaborators consisted. Web benjamin bloom led a team of researchers in the 1950s to establish behaviors associated with learning; In 1956, benjamin bloom headed a group of educational psychologists who developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior important in learning. Guide to the revised bloom’s taxonomy. Discover a list of action verbs that you can use to form learning objectives. Bloom. Solving problems by applying acquired knowl‐ edge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. This table of verbs lists cognitive processes that fit into bloom’s six categories and help identify the cognitive complexity or the order of thinking. While the overarching principles have remained the same, changes in understanding, experience and technology have seen the taxonomy take on a. Web what is bloom’s taxonomy? Web to use in a new situation. These “action words” describe the cognitive processes by which thinkers encounter and work with knowledge. Bloom found that over 95 % of the test questions students encounter require them to think only at the lowest possible level.the recall of information. *contents of this list compiled from the work. Web “since its publication in 1956, bloom’s taxonomy has been a foundation of most modern education systems. Web what is bloom’s taxonomy? The framework elaborated by bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing, abridged edition. Web comprehensive list of bloom's taxonomy verbs for use in ela, math, science, and social studies. Web the six levels of bloom's taxonomy are: Web bloom’s taxonomy is a system of hierarchical models (arranged in a rank, with some elements at the bottom and some at the top) used to categorize learning objectives into varying levels of complexity (bloom, 1956). Bloom found that over 95 % of the test questions students encounter require them to think. Solving problems by applying acquired knowl‐ edge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. Web bloom’s taxonomy is a hierarchical model that outlines six categories of learning and application skills that progress from less to more complex. Web to use in a new situation. *contents of this list compiled from the work of: Web benjamin bloom created a taxonomy. The outcome of this study was bloom’s taxonomy of learning (1956). Web additional information about bloom’s revised taxonomy is available here: Web comprehensive list of bloom's taxonomy verbs for use in ela, math, science, and social studies. Web what is bloom’s taxonomy? The framework elaborated by bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: This table of verbs lists cognitive processes that fit into bloom’s six categories and help identify the cognitive complexity or the order of thinking. These “action words” describe the cognitive processes by which thinkers encounter and work with knowledge. Web this printable table shows the progression of bloom's taxonomy, how each thinking skill applies in practice, and examples of activities using digital tools. Solving problems by applying acquired knowl‐ edge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. Web additional information about bloom’s revised taxonomy is available here: The first level is the most basic and involves identifying facts and concepts. The theory is based upon the idea that there are levels of observable actions that indicate something is happening in the brain (cognitive activity.) by creating learning objectives using. Web solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way. The framework elaborated by bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories: Making inferences and finding evidence to sup‐. A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing, abridged edition. Lower order thinking higher order thinking. The outcome of this study was bloom’s taxonomy of learning (1956). Knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation. Web benjamin bloom created a taxonomy of measurable verbs to help us describe and classify observable knowledge, skills, attitudes, behaviors and abilities. Discover a list of action verbs that you can use to form learning objectives.
Bloom's Taxonomy Preschool Set up Kidken Edu Solutions

FREE Blooms Taxonomy printable flipchart not an iLesson but very
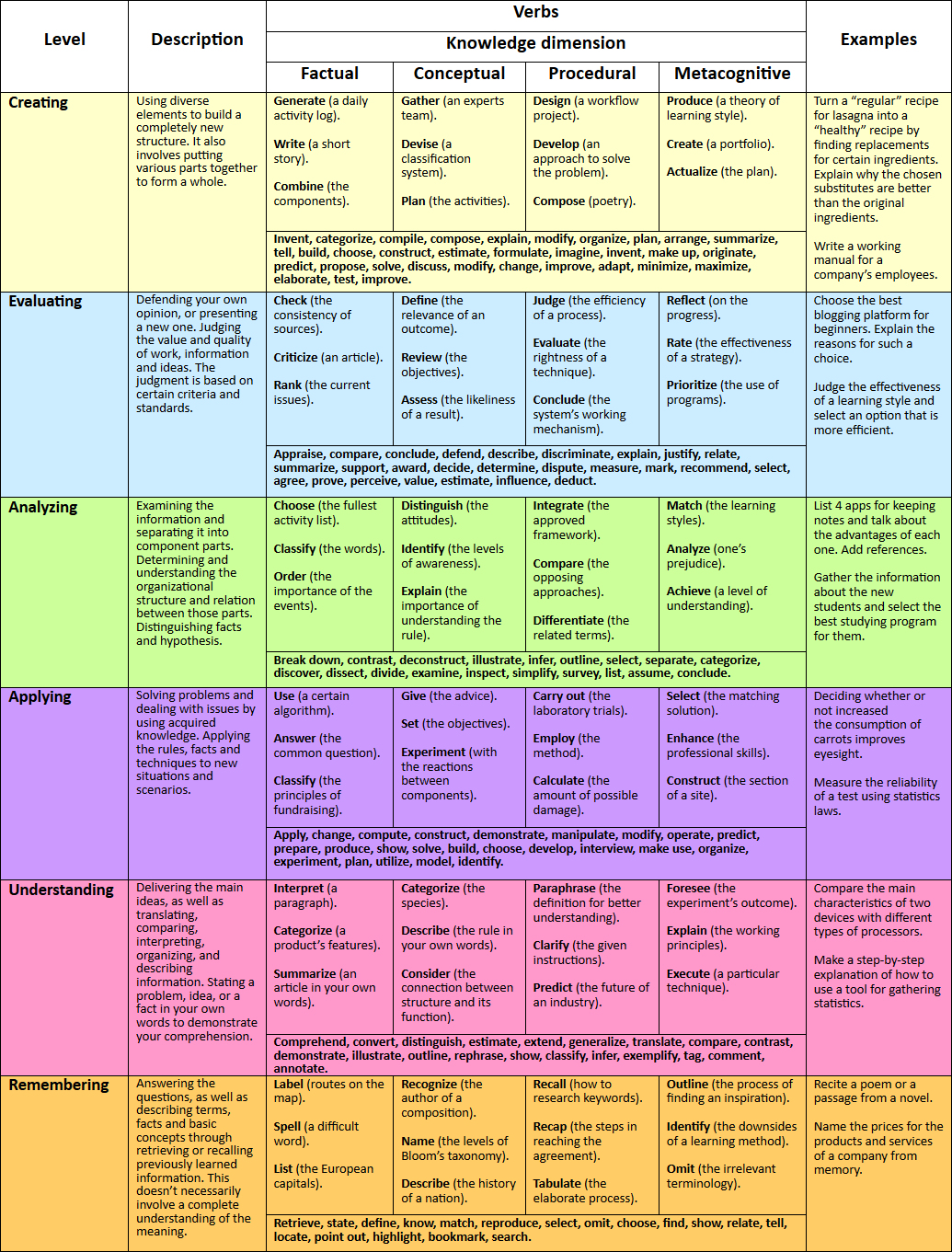
Bloom's Taxonomy—How to Make Your Studying Perfect?

Bloom's Taxonomy Verbs Free Classroom Chart
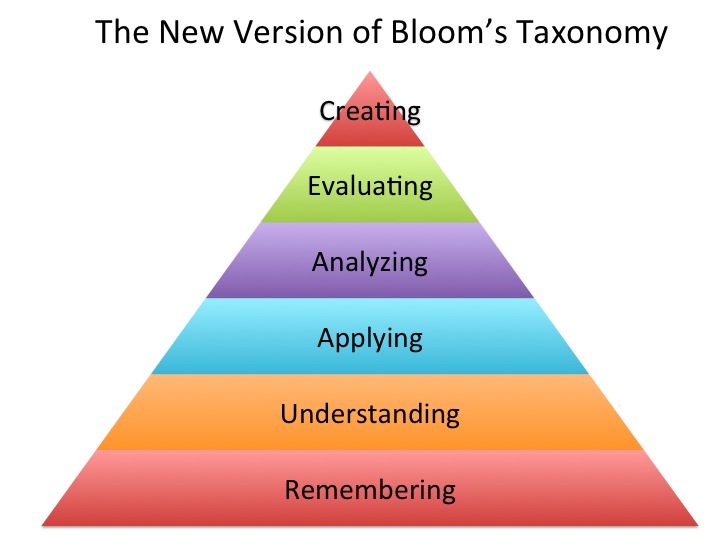
A Guide to Bloom’s Taxonomy The Innovative Instructor

wglink / Bloom's Triangles

Bloom's Taxonomy Graphic Aiming for HigherOrder Thinking
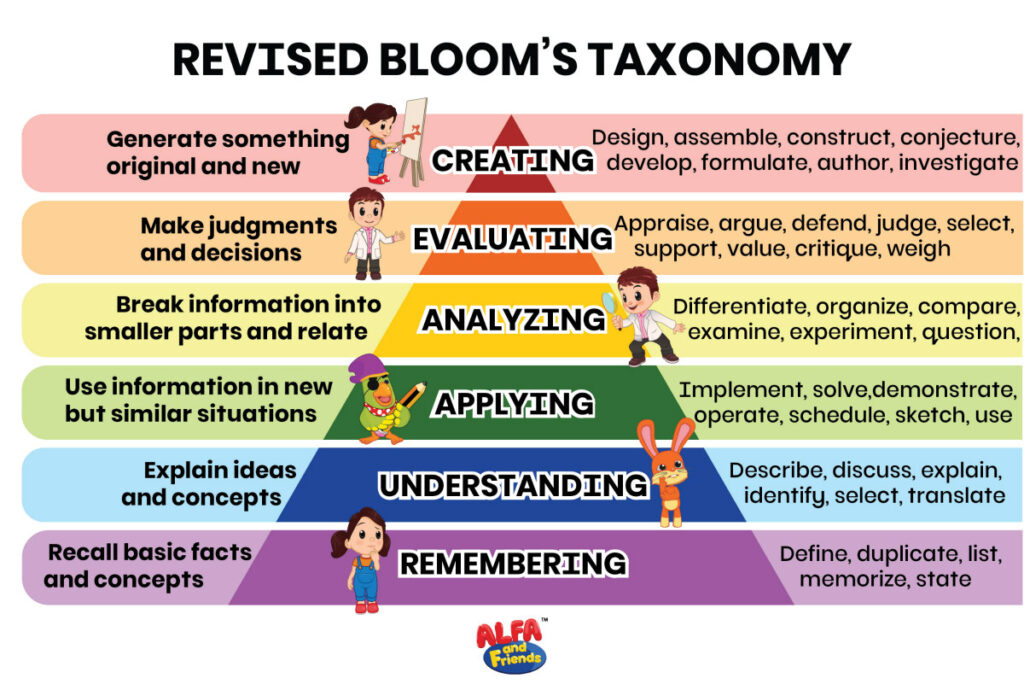
Using Bloom’s Taxonomy to Guide Interactions in the Classroom ALFA
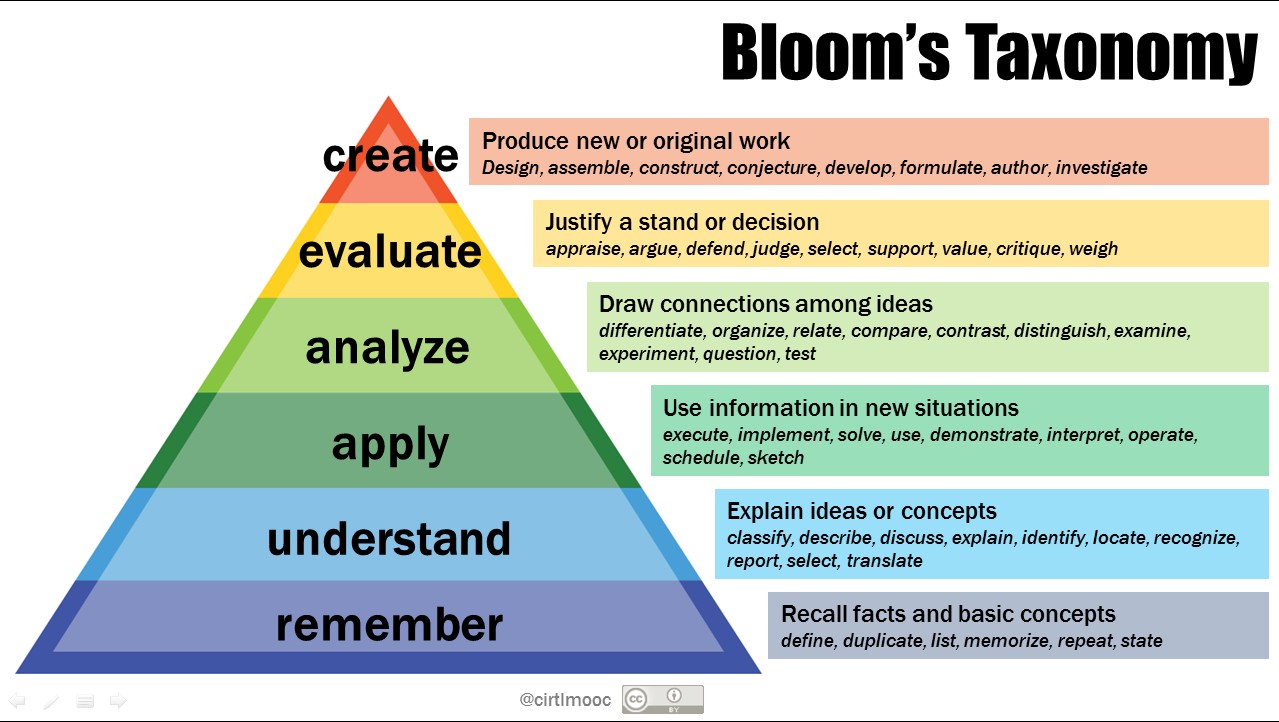
Bloom’s Taxonomy Center for Teaching Vanderbilt University

Bloom's Taxonomy Education Table
Web Benjamin Bloom Led A Team Of Researchers In The 1950S To Establish Behaviors Associated With Learning;
Web Comprehensive List Of Bloom's Taxonomy Verbs For Use In Ela, Math, Science, And Social Studies.
Examining And Breaking Information Into Parts By Identifying Motives Or Causes;
The Authors Of The Revised Taxonomy Underscore This Dynamism, Using Verbs And Gerunds To Label Their Categories And Subcategories (Rather Than The Nouns Of The Original Taxonomy).
Related Post: